 Antimicrobials, such as antibiotics, are substances used to kill microorganisms or to stop them from growing and multiplying. They are commonly used in human and veterinary medicine to treat a wide variety of infectious diseases. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) refers to the ability of microorganisms to withstand antimicrobial treatments. The overuse or misuse of antibiotics has been linked to the emergence and spread of microorganisms which are resistant to them, rendering treatment ineffective and posing a serious risk to public health. Resistant bacteria can spread through many routes. When AMR occurs in zoonotic bacteria present in animals and food it can also compromise the effective treatment of infectious diseases in humans.
Antimicrobials, such as antibiotics, are substances used to kill microorganisms or to stop them from growing and multiplying. They are commonly used in human and veterinary medicine to treat a wide variety of infectious diseases. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) refers to the ability of microorganisms to withstand antimicrobial treatments. The overuse or misuse of antibiotics has been linked to the emergence and spread of microorganisms which are resistant to them, rendering treatment ineffective and posing a serious risk to public health. Resistant bacteria can spread through many routes. When AMR occurs in zoonotic bacteria present in animals and food it can also compromise the effective treatment of infectious diseases in humans.
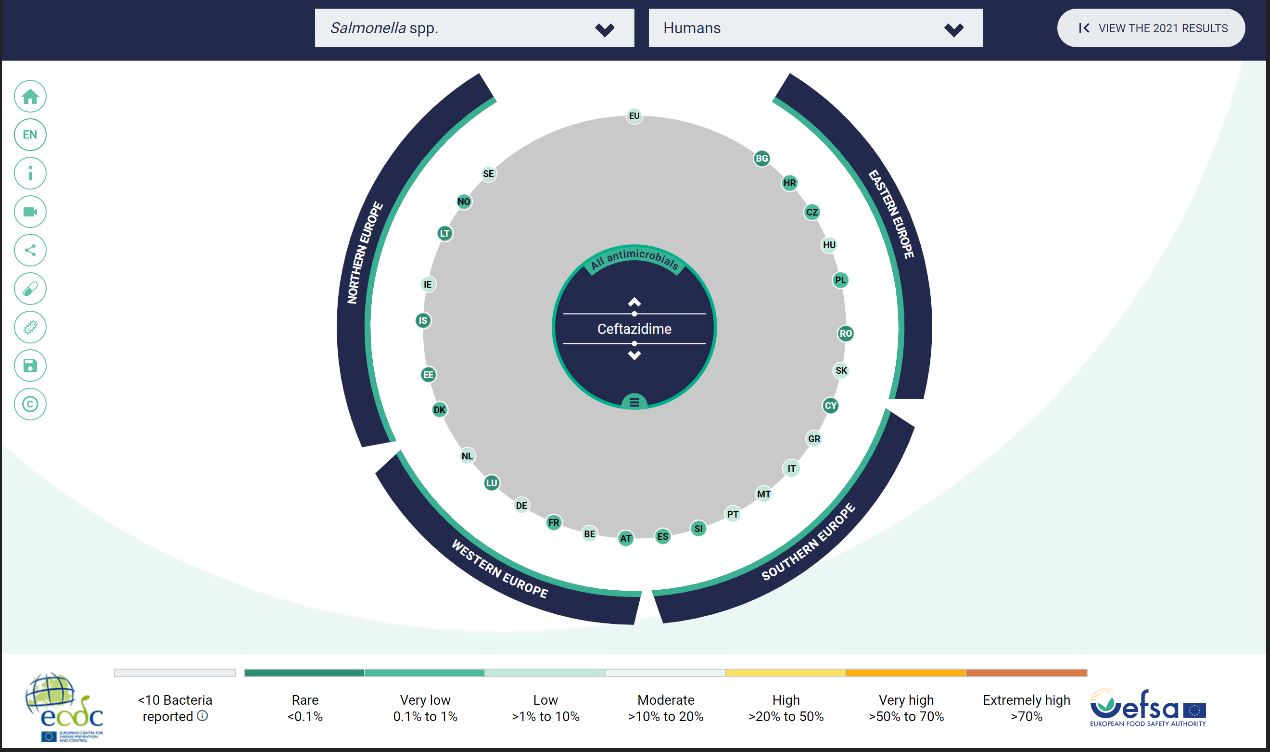
This interactive tool (data visualisation) is a simpler representation of the annual data concerning the resistance of Salmonella, E. Coli and Campylobacter in food, animals and humans, country by country collected by EFSA and ECDC from 2021-2022.
For more information click here
(Created by European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC)
Back to previous page